Imagine cruising down the road, windows down, music up, and suddenly, your car starts acting funny. The lights flicker, the radio cuts out, and a strange warning light illuminates on your dashboard. Electrical gremlins? Maybe. But the culprit could be something as simple – and often overlooked – as a blown alternator fuse.
A failing electrical system can leave you stranded and frustrated, especially when you're unprepared. Figuring out the cause of those mysterious symptoms can be a headache, and the thought of expensive repairs at the mechanic shop can add to the stress.
This guide will walk you through the process of identifying and replacing a blown alternator fuse. We'll cover the common symptoms, how to locate the fuse, and the steps for a successful replacement, so you can get back on the road with confidence.
In this article, we've explored the critical role of the alternator fuse, how to recognize the signs of a blown fuse, the simple steps to replace it, and some preventative measures to avoid future issues. Understanding these basics can save you time, money, and the frustration of being stranded with a dead battery. So, keep reading to empower yourself with the knowledge to tackle this common car problem. We delve into personal anecdotes, the history, myths, secrets, recommendations, fun facts, tips, and detailed guides about this topic.
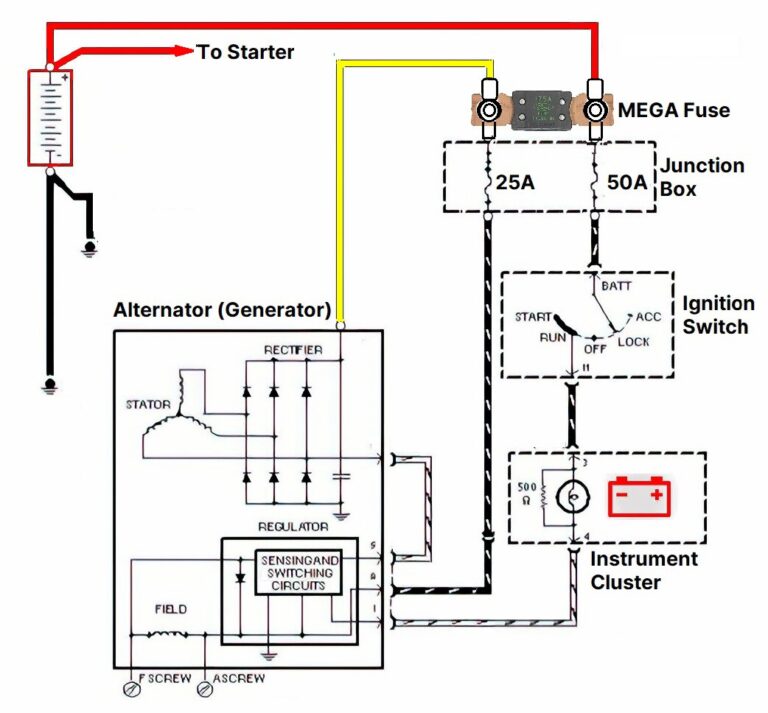
What is an Alternator Fuse and Why Does it Blow?
The alternator fuse serves a crucial protective function in your vehicle's electrical system. Its target is to shield the alternator from current overloads that could potentially damage it. I remember one time, my neighbor was experiencing continuous battery drainage issues. After numerous attempts to troubleshoot, we realized that the alternator fuse was frequently blowing, causing the alternator to work overtime.
This happened because the car had a short circuit, causing excessive current draw. We realized that the fuse was doing its job, preventing major damage to the alternator. The fuse is a sacrificial component that breaks the circuit when the current exceeds its rated capacity, thus preventing more costly damage. The blown alternator fuse is a key indicator of an underlying problem. The most common causes of blown alternator fuses include short circuits, overcharging, and component failures within the alternator itself. A worn-out voltage regulator, for instance, may lead to excessive voltage output, causing the fuse to blow. Similarly, damaged wiring can create a short circuit, leading to a surge of current. Identifying and addressing the root cause of the blown fuse is as important as replacing it.
Identifying a Blown Alternator Fuse
Identifying a blown alternator fuse is crucial for maintaining your vehicle's electrical health. This fuse, typically found in the fuse box under the hood or inside the car, is designed to protect the alternator from excessive current. When it blows, it can lead to various electrical issues, such as a dead battery, dimming headlights, and an inability to start the car. The first step in diagnosing a blown alternator fuse is to check the fuse box. Refer to your car's manual to locate the specific fuse related to the alternator. Visually inspect the fuse for any signs of damage, such as a broken filament or a dark, burnt mark. If the fuse looks intact, you can use a multimeter to test its continuity. Set the multimeter to the continuity setting (usually indicated by a sound wave symbol) and place the probes on each end of the fuse. If the multimeter beeps or shows a reading of zero ohms, the fuse is good. If there's no beep or the reading is infinite, the fuse is blown.
Symptoms of a blown alternator fuse can mimic other electrical problems, so it's essential to perform a thorough inspection. If you experience frequent fuse blowouts, it could indicate an underlying issue with the alternator or the wiring. In such cases, it's best to consult a professional mechanic to diagnose and fix the problem.
The History and Myths of the Alternator Fuse
The history of the alternator fuse is intertwined with the evolution of automotive electrical systems. Early automobiles relied on simple generators, but as vehicles became more complex, alternators replaced generators, providing a more efficient and reliable power source. With alternators came the need for protective devices like fuses to prevent damage from overcurrent. One common myth surrounding alternator fuses is that a blown fuse is always due to a faulty alternator. While alternator failure can indeed cause a fuse to blow, it's not the only reason. Short circuits, wiring issues, and even a faulty voltage regulator can also lead to a blown fuse. Another myth is that simply replacing the fuse will solve the problem. While this might provide a temporary fix, it's crucial to identify and address the underlying cause of the fuse blowout.
Failing to do so can result in repeated fuse failures and potentially more severe damage to the alternator or other electrical components. Understanding the true purpose and function of the alternator fuse can help dispel these myths and ensure proper diagnosis and repair. By debunking these myths, you can avoid unnecessary repairs and address the real issues causing the fuse to blow.
Hidden Secrets of the Alternator Fuse
One of the hidden secrets of the alternator fuse is its crucial role in protecting the entire electrical system of the vehicle. While it primarily safeguards the alternator, a blown fuse can also prevent damage to other sensitive components, such as the ECU (Engine Control Unit), sensors, and electronic accessories. Another lesser-known aspect of alternator fuses is their varying amperage ratings. Different vehicles and alternator types require different fuse sizes to provide adequate protection without causing nuisance tripping. Using the wrong amperage fuse can either result in frequent blowouts or inadequate protection. To determine the correct fuse size for your vehicle, consult the owner's manual or the fuse box diagram. Additionally, the location of the alternator fuse can vary depending on the vehicle make and model.
While it's commonly found in the main fuse box under the hood, some vehicles may have a secondary fuse box located inside the cabin or even near the alternator itself. Knowing the exact location of the fuse can save you time and effort when troubleshooting electrical issues. Lastly, regular inspection of the alternator fuse and its surrounding wiring can help identify potential problems before they lead to a complete failure. Look for signs of corrosion, loose connections, or damaged insulation, and address them promptly to ensure the reliability of your vehicle's electrical system.
Recommendations for Maintaining Your Alternator Fuse
Maintaining your alternator fuse is a proactive approach to ensuring the longevity and reliability of your vehicle's electrical system. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. Start by visually inspecting the fuse box for any signs of corrosion, loose connections, or damaged wiring. Clean any corrosion with a wire brush and ensure that all connections are tight and secure. Another important recommendation is to replace the alternator fuse with the correct amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage can overload the circuit and damage the alternator or other components, while using a fuse with a lower amperage can cause nuisance tripping.
Consult your vehicle's owner's manual or the fuse box diagram to determine the correct fuse size. Additionally, consider carrying spare fuses in your vehicle in case of a blown fuse. This can save you time and frustration if you experience an electrical issue while on the road. Finally, if you notice frequent fuse blowouts, it's essential to have the underlying cause diagnosed by a professional mechanic. Repeatedly replacing the fuse without addressing the root problem can lead to more severe damage and costly repairs.
Tools and Materials Needed for Replacement
Replacing an alternator fuse is a straightforward task that can be accomplished with a few essential tools and materials. Before starting, make sure to gather the following items: a set of pliers or fuse puller, a new alternator fuse with the correct amperage rating, a multimeter for testing continuity, and your vehicle's owner's manual or fuse box diagram. The pliers or fuse puller will help you remove the blown fuse from the fuse box without damaging the surrounding components. A new alternator fuse with the correct amperage rating is crucial for ensuring proper protection of the alternator. Using the wrong amperage can lead to either nuisance tripping or inadequate protection. The multimeter is used to test the continuity of the fuse to confirm whether it's blown. Set the multimeter to the continuity setting and place the probes on each end of the fuse. If the multimeter beeps or shows a reading of zero ohms, the fuse is good. If there's no beep or the reading is infinite, the fuse is blown. Your vehicle's owner's manual or fuse box diagram will provide valuable information about the location of the alternator fuse and the correct amperage rating.
Having these tools and materials on hand will make the replacement process smoother and more efficient. Remember to always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on the electrical system to prevent accidental short circuits or electrical shocks.
Tips for Preventing a Blown Alternator Fuse
Preventing a blown alternator fuse involves proactive measures to maintain your vehicle's electrical system. Regularly inspect the wiring for any signs of damage, such as frayed insulation or loose connections. Address any issues promptly to prevent short circuits, which are a common cause of blown fuses. Another tip is to avoid overloading the electrical system with too many accessories. Adding excessive aftermarket accessories, such as high-powered audio systems or auxiliary lights, can strain the alternator and lead to overcurrent, causing the fuse to blow. If you need to install additional accessories, ensure that they are properly wired and fused to prevent overloading the system. Additionally, avoid running the battery down completely, as this can put extra stress on the alternator when it tries to recharge the battery. Regularly check the battery voltage and charge it if it's consistently low.
Furthermore, consider having your vehicle's electrical system inspected by a professional mechanic periodically. They can identify potential issues before they lead to a blown fuse or other electrical problems. By following these tips, you can significantly reduce the risk of experiencing a blown alternator fuse and ensure the reliability of your vehicle's electrical system.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the Fuse
Replacing an alternator fuse is a simple task that can be performed with a few basic tools. Follow these step-by-step instructions to safely and effectively replace a blown alternator fuse: First, locate the fuse box in your vehicle. It's typically located under the hood or inside the cabin. Consult your vehicle's owner's manual or the fuse box diagram to identify the specific fuse related to the alternator. Next, disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent accidental short circuits or electrical shocks. Use a wrench to loosen the nut on the negative terminal and carefully remove the cable. Remove the fuse box cover and use a fuse puller or pliers to gently remove the blown fuse. Inspect the fuse for any signs of damage, such as a broken filament or a dark, burnt mark. If the fuse looks intact, use a multimeter to test its continuity. Set the multimeter to the continuity setting and place the probes on each end of the fuse. If the multimeter beeps or shows a reading of zero ohms, the fuse is good. If there's no beep or the reading is infinite, the fuse is blown. Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Ensure that the new fuse is securely seated in the fuse box.
Reattach the fuse box cover and reconnect the negative battery terminal. Tighten the nut on the negative terminal to ensure a secure connection. Finally, start the engine and check if the electrical system is functioning properly. If you continue to experience issues, it's best to consult a professional mechanic.
Fun Facts About Alternator Fuses
Did you know that alternator fuses come in various shapes and sizes? These fuses, designed to protect your vehicle's electrical system, are not one-size-fits-all. They range from small blade-type fuses to larger cartridge-style fuses, each with different amperage ratings to suit specific vehicle requirements. Another fun fact is that the alternator fuse is often overlooked during routine maintenance. While many car owners focus on oil changes and tire rotations, the alternator fuse plays a crucial role in maintaining the vehicle's electrical health. Neglecting to check the fuse can lead to unexpected electrical issues and potentially leave you stranded. Interestingly, the alternator fuse is a sacrificial component. It's designed to blow and break the circuit when there's an overcurrent, protecting the more expensive and critical alternator from damage. This simple fuse can save you from costly repairs by preventing major electrical failures.
Additionally, the location of the alternator fuse can vary depending on the vehicle make and model. While it's commonly found in the main fuse box under the hood, some vehicles may have a secondary fuse box located inside the cabin or even near the alternator itself. Knowing the exact location of the fuse can save you time and effort when troubleshooting electrical issues.
How to Check Your Alternator Fuse
Checking your alternator fuse is a simple yet essential task that can help you diagnose electrical issues in your vehicle. First, locate the fuse box, which is typically found under the hood or inside the cabin. Consult your vehicle's owner's manual or the fuse box diagram to identify the specific fuse related to the alternator. Once you've located the fuse, visually inspect it for any signs of damage, such as a broken filament or a dark, burnt mark. If the fuse looks intact, you can use a multimeter to test its continuity. Set the multimeter to the continuity setting (usually indicated by a sound wave symbol) and place the probes on each end of the fuse. If the multimeter beeps or shows a reading of zero ohms, the fuse is good. If there's no beep or the reading is infinite, the fuse is blown.
If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Ensure that the new fuse is securely seated in the fuse box. If you're unsure how to perform these steps, consult a professional mechanic. Regularly checking your alternator fuse can help you identify potential electrical problems early on and prevent more severe damage to your vehicle's electrical system.
What Happens If You Don't Replace a Blown Alternator Fuse?
If you neglect to replace a blown alternator fuse, several issues can arise, potentially leading to more significant problems. The most immediate consequence is a non-charging battery. The alternator is responsible for charging the battery while the engine is running, and a blown fuse prevents it from doing so. Over time, the battery will drain completely, leaving you stranded with a dead car. In addition to a dead battery, a blown alternator fuse can also affect other electrical components in your vehicle. The alternator provides power to various systems, such as the headlights, radio, and air conditioning. Without a functioning alternator, these systems may not operate properly or at all.
Driving with a blown alternator fuse can also put additional strain on the battery, as it's forced to supply all the electrical power needed to run the vehicle. This can shorten the battery's lifespan and potentially lead to premature failure. Furthermore, ignoring a blown alternator fuse can mask underlying issues with the alternator or the electrical system. The fuse is designed to protect the alternator from overcurrent, and if it blows repeatedly, it could indicate a more serious problem. It's essential to diagnose and address the root cause of the fuse blowout to prevent further damage and costly repairs.
Listicle of Common Alternator Fuse Issues
Here's a listicle of common alternator fuse issues that you might encounter:
1.Frequent Fuse Blowouts: If your alternator fuse blows repeatedly, it indicates an underlying problem in your electrical system. Common causes include short circuits, overloads, or a faulty alternator.
2.Corrosion: Corrosion on the fuse or the fuse box terminals can disrupt the electrical connection and cause the fuse to blow prematurely.
3.Loose Connections: Loose connections can cause voltage drops and increased resistance, leading to overheating and fuse failure.
4.Incorrect Fuse Rating: Using a fuse with the wrong amperage rating can either result in nuisance tripping or inadequate protection.
5.Damaged Wiring: Damaged wiring, such as frayed insulation or exposed wires, can cause short circuits and blow the fuse.
6.Overloading the System: Adding too many electrical accessories can overload the alternator and cause the fuse to blow.
7.Alternator Failure: A faulty alternator can draw excessive current and blow the fuse.
8.Voltage Regulator Issues: A malfunctioning voltage regulator can cause overcharging and blow the fuse.
9.Battery Problems: A weak or failing battery can put extra strain on the alternator, leading to fuse failure.
10.Environmental Factors: Exposure to extreme temperatures, moisture, or chemicals can accelerate fuse degradation and failure.
Question and Answer Section
Here are some frequently asked questions about alternator fuses:
Q: How do I know if my alternator fuse is blown?
A: Common symptoms include a dead battery, dimming headlights, and an inability to start the car. Visually inspect the fuse for a broken filament or use a multimeter to test its continuity.
Q: Can I use a higher amperage fuse to prevent it from blowing again?
A: No, using a higher amperage fuse can overload the circuit and damage the alternator or other components. Always use the correct amperage rating specified in your vehicle's owner's manual.
Q: What causes an alternator fuse to blow repeatedly?
A: Frequent fuse blowouts indicate an underlying problem, such as a short circuit, overload, or a faulty alternator. Have a professional mechanic diagnose and fix the issue.
Q: Where is the alternator fuse located?
A: The alternator fuse is typically located in the fuse box under the hood or inside the cabin. Consult your vehicle's owner's manual or the fuse box diagram to identify the specific fuse.
Conclusion of Blown Alternator Fuse: Identifying and Replacing It
Understanding the alternator fuse, its function, and how to identify and replace it is a valuable skill for any car owner. By recognizing the symptoms of a blown fuse, knowing the proper replacement procedure, and taking preventative measures, you can avoid being stranded and ensure the reliability of your vehicle's electrical system. Remember to always use the correct amperage fuse, inspect the wiring regularly, and address any underlying issues promptly. With this knowledge, you can confidently tackle this common car problem and keep your vehicle running smoothly. This ultimately contributes to road safety and vehicle maintenance.