Ever wondered why some cars feel like they're glued to the road while others seem to float over every bump? A surprising factor plays a huge role: weight. But pinning down exactly how much the average car weighs isn't as straightforward as you might think.
Thinking about car weight often comes up when you're considering fuel efficiency, safety ratings, or even just comparing the feel of different vehicles. You might be curious about how weight impacts performance, or maybe you're trying to understand how heavier electric vehicles manage their battery range. Figuring out the average car weight and what influences it can feel like navigating a complex maze of numbers and specs.
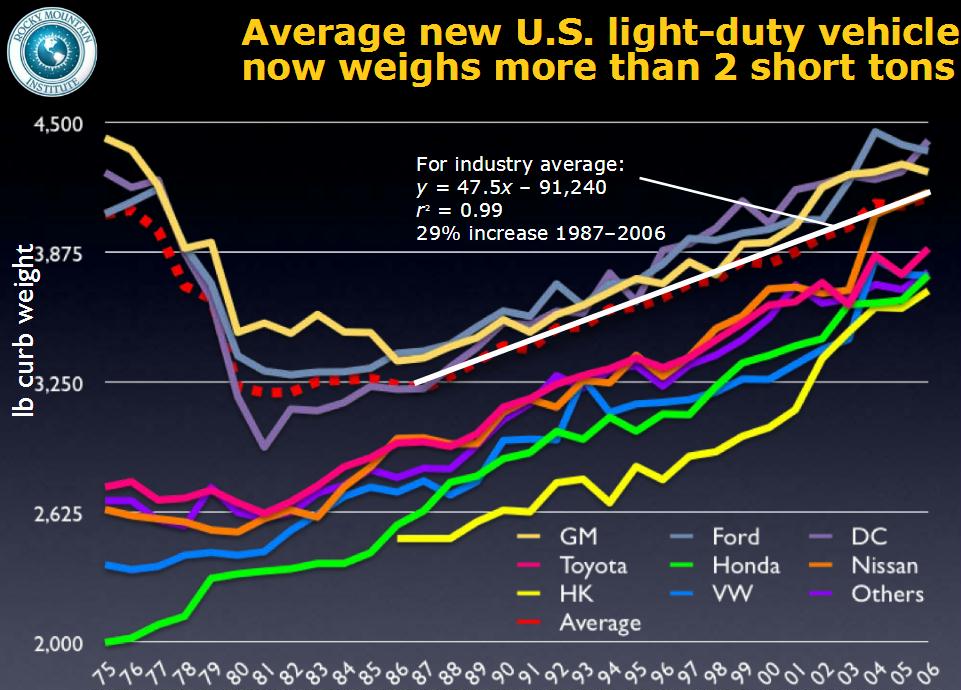
So, what's the bottom line? The average car weight in 2024 hovers around 4,100 pounds (1,860 kilograms). However, this is just an average. The actual weight can vary dramatically based on vehicle type, size, features, and the materials used in its construction. Let's dive into the factors that contribute to these weight differences.
Understanding the average car weight requires considering various vehicle types, from compact cars to SUVs and trucks. Material choices, safety features, and even the inclusion of advanced technology all contribute to the overall figure. Knowing these factors helps you make informed decisions, whether you're a car buyer, an automotive enthusiast, or just curious about the mechanics of modern vehicles.
Factors Influencing Car Weight
The weight of a car isn't just a random number; it's a result of many different design choices and material considerations. I remember helping a friend move once. He had a tiny, older hatchback, and I had a newer, much larger sedan. We were both surprised at how much lighter his car felt when we were pushing it (don't ask!). That experience really highlighted how much car design has changed and how it affects weight.
One of the biggest factors is thevehicle class. A subcompact car like a Mini Cooper will naturally weigh significantly less than a full-size SUV like a Chevrolet Suburban. The SUV needs a larger engine, a more robust frame, and more interior components to accommodate passengers and cargo. Sedans typically fall somewhere in the middle.
Then there's thematerials used in construction. Older cars often relied heavily on steel, which is strong but heavy. Modern cars are increasingly using aluminum, high-strength steel, and even carbon fiber in some high-performance models. These materials offer comparable strength with a significant weight reduction. This is particularly important for electric vehicles where every pound saved translates to increased range.
Finally, thefeatures included in the vehiclecan also add weight. Luxury features like heated seats, advanced sound systems, and large infotainment screens all contribute to the overall weight. Even safety features like airbags, reinforced doors, and anti-lock braking systems add pounds to the vehicle.
Understanding Curb Weight vs. Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR)
When discussing car weight, it's crucial to understand the difference between "curb weight" and "gross vehicle weight rating" (GVWR). Curb weight refers to the weight of the vehicle as it sits, ready to drive, with all fluids filled to capacity but without any passengers or cargo. Think of it as the car's "empty" weight.
GVWR, on the other hand, represents the maximum allowable weight of the vehicle, including the curb weight plus the weight of passengers, cargo, and any accessories. This number is important because exceeding the GVWR can compromise the vehicle's handling, braking, and overall safety. You'll typically find the GVWR listed on a sticker inside the driver's side doorjamb.
Knowing these two figures is essential for safe loading and operation. If you regularly haul heavy loads, it's vital to choose a vehicle with a GVWR that comfortably accommodates the weight of your cargo and passengers. Ignoring the GVWR can lead to increased wear and tear on the vehicle, reduced fuel economy, and potentially dangerous driving conditions.
For example, a pickup truck with a GVWR of 6,000 pounds and a curb weight of 4,000 pounds can safely carry a combined weight of 2,000 pounds of passengers and cargo. Understanding these limits is crucial for safe and responsible vehicle operation.
A Brief History of Car Weight: From Heavy Metal to Lightweight Innovation
The history of car weight is a fascinating reflection of technological advancements and evolving design philosophies. Early automobiles were undeniably heavy, often constructed with bulky steel frames and massive engines. Think of those classic cars from the early 20th century – they were built like tanks!
As automotive technology progressed, engineers began exploring ways to reduce weight without sacrificing safety or performance. The introduction of unibody construction, where the body and frame are integrated into a single unit, was a significant step in this direction. This design offered improved structural integrity while reducing overall weight compared to traditional body-on-frame designs.
The oil crises of the 1970s further accelerated the drive towards lighter vehicles. Automakers were forced to improve fuel efficiency, and weight reduction became a key strategy. This led to increased use of aluminum and plastics in vehicle construction. Today, the focus is on even more advanced materials like carbon fiber and magnesium alloys, which offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios. The rise of electric vehicles has also heightened the importance of weight reduction, as lighter cars can achieve longer driving ranges.
The Hidden Secret to Car Weight: It's Not Just About Size
While size is an obvious factor in determining car weight, there's a hidden secret: it's not theonlydeterminant. Seemingly identical vehicles can have surprising weight differences due to seemingly small variations in equipment and design choices.
For example, the choice of wheels can make a noticeable difference. Alloy wheels are often lighter than steel wheels, which can improve handling and fuel economy. Similarly, the type of glass used in the windows can affect weight. Laminated glass, which is used in windshields for safety, is heavier than tempered glass.
Even the type of seats can play a role. Leather seats are typically heavier than cloth seats due to the extra material and padding. And don't forget about the electronics! Modern cars are packed with sensors, computers, and wiring, all of which contribute to the overall weight. The complexity of these systems can lead to surprising weight differences between different trim levels of the same model.
Recommendations for Managing Car Weight and Fuel Efficiency
If you're concerned about car weight and its impact on fuel efficiency, there are several steps you can take to manage it effectively. First and foremost, consider your driving needs when choosing a vehicle. Do you really need a large SUV, or would a smaller, more fuel-efficient sedan suffice? Choosing the right vehicle for your lifestyle is the first step towards optimizing fuel economy.
Next, be mindful of the cargo you carry. Carrying unnecessary weight in your car can significantly reduce fuel efficiency. Remove any items you don't need on a regular basis, such as sporting equipment, tools, or extra clothing. Regularly cleaning out your trunk can make a surprising difference.
Finally, pay attention to your driving habits. Aggressive driving, such as rapid acceleration and hard braking, consumes more fuel and puts more strain on the vehicle. Driving smoothly and maintaining a steady speed can improve fuel economy and extend the life of your car.
The Impact of Electric Vehicle Batteries on Overall Weight
Electric vehicles (EVs) present a unique challenge when it comes to weight. While EVs eliminate the heavy internal combustion engine, they introduce a new weight factor: the battery pack. EV batteries are substantial components, often weighing hundreds of pounds, and they significantly impact the overall weight of the vehicle.
The size and type of battery directly affect the range of the EV. Larger batteries provide more range but also add more weight. Automakers are constantly working to improve battery technology, developing lighter and more energy-dense batteries to increase range without adding excessive weight. This is a critical area of innovation in the EV industry.
The placement of the battery pack also affects the vehicle's handling and stability. Many EVs mount the battery pack low in the chassis, which helps to lower the center of gravity and improve handling. However, this low placement can also reduce ground clearance and make the vehicle more susceptible to damage from road hazards.
Tips for Reducing Car Weight (Without Sacrificing Safety)
While drastically altering your car's weight might not be feasible, there are some minor adjustments you can make to shave off a few pounds without compromising safety. For example, consider replacing heavy steel wheels with lighter alloy wheels. This can improve handling and acceleration, as well as slightly improve fuel economy.
Another option is to remove any unnecessary items from your car. Cleaning out your trunk and glove compartment can eliminate excess weight. Consider replacing heavy floor mats with lighter alternatives. Every little bit helps!
It's important to emphasize that safety should always be your top priority. Avoid removing or modifying any safety-critical components, such as airbags, seatbelts, or structural elements of the vehicle. Focus on removing non-essential items and making minor upgrades that improve performance without compromising safety.
How Car Weight Affects Braking Distance
Car weight has a direct impact on braking distance. A heavier vehicle requires more force to stop, which translates to longer braking distances. This is particularly important in emergency situations where every foot counts.
The relationship between weight and braking distance is governed by the laws of physics. Heavier vehicles have more momentum, meaning they require more force to decelerate at the same rate as lighter vehicles. This means that a heavier car will take longer to stop, all other factors being equal.
Factors such as tire condition, road surface, and braking system performance also influence braking distance. However, weight remains a significant factor. Drivers of heavier vehicles should be aware of the increased stopping distances and adjust their driving accordingly.
Fun Facts About Car Weight Throughout History
Did you know that the average car weight has fluctuated significantly over the years? In the early days of automotive manufacturing, cars were relatively heavy due to the use of steel and cast iron. However, as manufacturers began experimenting with lighter materials, such as aluminum and plastics, the weight of cars began to decrease.
During the oil crises of the 1970s, there was a renewed focus on fuel efficiency, leading to further weight reduction efforts. However, as safety regulations and consumer demand for larger vehicles increased, car weights began to creep back up. Today, the average car weight is higher than it was in the 1970s, but manufacturers are constantly innovating to find new ways to reduce weight without compromising safety or performance.
Another fun fact is that the heaviest production car ever made was the Bugatti Royale, which weighed over 7,000 pounds! This luxurious vehicle was built in the 1920s and 1930s and was designed for royalty. In contrast, the lightest production car ever made was the Peel P50, which weighed just 130 pounds!
How to Find Your Car's Weight
Finding your car's weight is usually a pretty straightforward process. The most reliable source is your vehicle's owner's manual. Look for a section that lists specifications, and you should find the curb weight clearly stated. This is the weight of the vehicle with all fluids topped off, but without passengers or cargo.
Another place to find the weight is on the driver's side doorjamb. There's usually a sticker there that lists the vehicle's GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating), as well as other important information. While the GVWR isn't the same as the curb weight, it can be helpful to know both figures.
If you can't find the weight in either of those places, you can also try searching online. Many websites and databases provide vehicle specifications, including weight. Just make sure you're using a reliable source and that the information is specific to your vehicle's year, make, and model.
What If Car Weight Could Be Magically Reduced?
Imagine a world where the weight of cars could be magically reduced without affecting their safety, performance, or structural integrity. What would be the implications? For starters, fuel efficiency would skyrocket. Lighter cars require less energy to accelerate and maintain speed, which would translate to significant fuel savings for drivers.
Handling and performance would also improve. Lighter cars are more nimble and responsive, making them more fun to drive. Braking distances would be shorter, and cornering ability would be enhanced.
Electric vehicles would also benefit greatly. Lighter EVs would have longer driving ranges, making them more practical for long trips. The need for massive battery packs would be reduced, which would lower the cost of EVs and make them more accessible to consumers. It's a fascinating thought experiment to consider!
Top 5 Lightest Cars on the Market (and Why They're So Efficient)
Here's a list of the top 5 lightest cars currently available on the market, along with some reasons why they achieve such impressive fuel efficiency:
- Mitsubishi Mirage G4: Weighing in at around 2,100 pounds, the Mirage G4 is a subcompact sedan known for its exceptional fuel economy. Its lightweight design, combined with a small and efficient engine, allows it to achieve impressive gas mileage.
- Nissan Versa: The Nissan Versa is another subcompact sedan that prioritizes fuel efficiency. With a weight of around 2,500 pounds, it offers a good balance of practicality and economy.
- Kia Rio: The Kia Rio is a subcompact hatchback that offers a stylish design and a comfortable ride. Its lightweight construction contributes to its impressive fuel economy.
- Hyundai Accent: The Hyundai Accent is a subcompact sedan that's known for its value and efficiency. With a weight of around 2,600 pounds, it's a great option for budget-conscious drivers.
- Mazda MX-5 Miata: While not primarily focused on fuel economy, the Mazda MX-5 Miata is a lightweight sports car that delivers a fun and engaging driving experience. Its low weight contributes to its nimble handling and responsive performance.
Question and Answer Section
Q: How does car weight affect fuel efficiency?
A: Car weight has a significant impact on fuel efficiency. Heavier vehicles require more energy to accelerate and maintain speed, which translates to lower fuel economy. Lighter vehicles are more fuel-efficient.
Q: What is the difference between curb weight and GVWR?
A: Curb weight is the weight of the vehicle with all fluids filled, but without passengers or cargo. GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating) is the maximum allowable weight of the vehicle, including the curb weight plus the weight of passengers, cargo, and accessories.
Q: What are some ways to reduce car weight?
A: Some ways to reduce car weight include using lighter materials like aluminum and carbon fiber, removing unnecessary items from the vehicle, and choosing lighter wheels and tires.
Q: How does car weight affect braking distance?
A: Car weight affects braking distance by increasing the distance required to stop. A heavier vehicle requires more force to decelerate, resulting in longer braking distances.
Conclusion of What is the Average Car Weight?
Understanding the average car weight and the factors that influence it is crucial for making informed decisions as a car buyer or enthusiast. From the choice of materials to the inclusion of advanced features, every element contributes to the overall weight and, consequently, to the vehicle's performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. By considering these factors, you can better appreciate the complexities of automotive design and make choices that align with your needs and preferences.